The head of state, Kassym-Jomart Tokayev, at the fourth meeting of the National Council of Public Trust in October 2020, announced a decision to proclaim 2021 as the Year of the 30th Anniversary of Independence.
If you delve into the history of the country, October 25, 1990 is the day of sovereignty, which became a turning point in Kazakhstan’s history. The first fundamental legislative act of the country was the Declaration of Independence. It is a legal, political and ideological document that reflects the basic principles of the public, human rights and freedoms, property, political pluralism and separation of powers. These fundamental investments formed the basis of the Constitution.
On December 16, 1991, Kazakhstan adopted the Constitutional Law on Independence in the Republic of Kazakhstan.
Independence Day is a symbol of freedom and greatness of our country. And it is of great importance for every citizen of Kazakhstan.
During this short period of time, the country has developed very dynamically and has achieved tremendous success. For 30 years, we have managed to build a stable economy, science, and also succeed in the social sphere, politics, culture, and sports.
The field of science is an important aspect of the rapid development of the state, which has a huge impact on both the internal and external economy of the country. One of the most important industries is the food and processing industry in the agro-industrial complex.
In his Address to the people of Kazakhstan on September 1, 2020, the Head of State called the most important task – the full disclosure of the country’s industrial potential. In this regard, the Government has been tasked with increasing the competitiveness of manufacturing enterprises in the domestic and foreign markets.
The industry of any state is a symbiosis of branches of material production. Their functions are in the extraction of raw materials, the production and processing of materials and energy, the manufacture of machines, various goods, as well as the provision of services to the population.
The Ministry of Industrialization and Infrastructure Development of the Republic of Kazakhstan, together with the regions, has formed Industrialization Maps, taking into account the specifics and competitive advantages of regions that cover various industrial sectors. For 2020, in the regions, it was planned to commission 206 projects for a total amount of 995 billion tenge with the creation of more than 18 thousand new permanent jobs.
In terms of industries, the largest number of new industries in the agro-industrial complex and the food industry – 76 projects, building materials and mechanical engineering – 38 and 19 projects, respectively.
The processing of agricultural raw materials, as well as the production of high-quality, affordable and competitive food products are among the priority tasks of the agro-industrial complex in ensuring the country’s food security, which contributes to improving the economic condition of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
It should be noted that over the years of Independence in the Republic of Kazakhstan there has been a colossal and rapid growth in the agro-industrial complex, despite the collapse of small and large enterprises, factories, workshops in the Kazakh SSR and the restructuring of the country.
According to statistics, the total income from the export of agricultural products in Kazakhstan in 2018 amounted to 3.02 billion dollars. USD 3.2 billion in 2019, USD 3.5 billion in 2020. There is a positive trend and it is planned by 2025. increase export income to US $ 5.1 billion (Fig. 1).
.
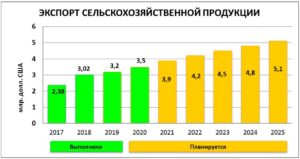
Figure 1 – Export of agricultural products of the Republic of Kazakhstan
But, unfortunately, a high level of imports remains for the main types of food: for cheeses and cottage cheese (47%), for sausages (40%), for canned meat and meat-vegetable products (51%), for processed fish (49%) and butter (36%) (Fig. 2).).
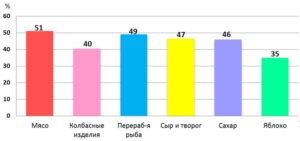
Figure 2 – Import of food products to the Republic of Kazakhstan
Each link in the field-to-table chain has its own level of profitability. The main locomotive of profitability is the processing and food industries. Hence the conclusion that the satisfaction of the domestic market and the growth of income from the export of agricultural products should be expected only from the effective deep processing of agricultural raw materials.
The information in Table 1 reflects the target consumer markets for highly processed grain products – starch products. In value terms, starch product markets are as follows: bioethanol about $ 75 billion, starch about $ 25.7 billion, syrups and modified starches about $ 33 billion, amino acids over $ 6.5 billion It reached 8.5 million tons in 2017. It is expected that the market volume will reach 11 million tons in 2023. The dynamics in such a short period may be due to the intensive development of the production of amino acids and organic acids, as well as the rapid development of animal husbandry – the main consumer of amino acids.
.
Table 1 – Capacity of the world market of starch products in physical terms
| Demand for carbohydrates (in the form of starch) t / year | |
| Bioethanol | 180 million |
| Крахмал | 73 million |
| GFS, syrups | 18 million |
| Modif, starches | 13million |
| Biochemicals | 8,5 million |
| Amino acids | 3,9 million |
| Organic acids | 2,6 million |
| Sorbitol | 800 000 |
| Antibiotics | 500 000 |
| Yeast | 3,6 million |
| Bioplastic | 2 million |
A significant increase in production and consumption, according to Global Market Insights, will be shown by the biopolymer market, as the market value of biopolymer films by 2025 will exceed US $ 6.7 billion (main consumers of China, India).
Our calculations for the deep processing of wheat grain (Fig. 3) showed that from 1 ton of wheat grain at a price of 86.0 thousand tenge. with its deep processing, you can get dry gluten, glucose-fructose syrup, modified starch and bran for feed – for a total of 283.6 thousand tenge, which is almost 3.5 times higher than the cost of grain. That is, with the export of processed wheat grain products weighing 5.0 million tons, they would have a revenue of about 4.0 billion US dollars, instead of 1.22 billion US dollars And this, accordingly, new jobs and stable demand for agricultural products, and the overall growth of the country’s economy.
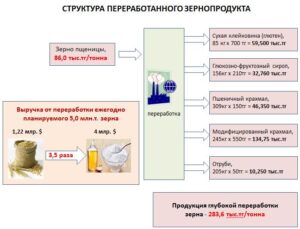
Figure 3 – Structure of processed grain product
According to Oil World analysts, in 2018-19. Kazakhstan has become a leader not only in terms of sown areas – 1.1 million hectares, but also in the production of oilseed flax, having collected a record harvest of 780 thousand tons, while overtaking Russia and Canada. The high demand of the largest world importer of culture – the EU – for Kazakh flax allows the republic not to experience difficulties in selling the oilseed crop, and also to increase export volumes from year to year (Fig. 4).
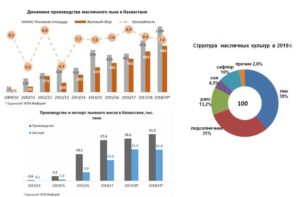
Figure 4 – Current situation of oilseed flax production in the Republic of Kazakhstan
Today, in the world practice, deep processing of oil flax produces the following products: lecithin – an organic, fat-like compound, which, in turn, is the richest source of a whole complex of phospholipids, are used in the food industry and pharmaceuticals; drying oil – made from linseed oil with the addition of a desiccant, intended for diluting thick-grated oil paints used for interior work; Linseed wool is a cheap substitute for traditional cotton wool, obtained from oil flax waste, and is used in medicine. Figure 5 provides information on the structure of oilseed flax processing.
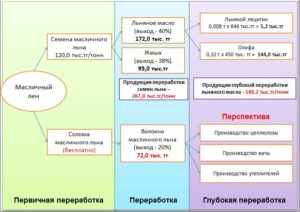
Figure 5 – Structure of oilseed flax processing
One ton of oil flax seeds costs 120 thousand tenge, 400 kg of flaxseed oil, 380 kg of oil cake are obtained from it for a total of 267 thousand tenge. From linseed oil by deep processing it is possible to obtain edible lecithin and drying oil in the amount of 149.2 thousand tenge.
Oil flax straw is currently not processed at all, but remains in the fields and burned. With the complex processing of oil flax, from 1 ton of straw, 20 kg of natural fiber can be obtained for 72 thousand tenge. (1 ton of fiber costs 360 thousand tenge). Further, the fiber of oilseed flax can be used for the production of cellulose, cotton wool and insulation.
In the structure of deep processing of cattle slaughter products, meat and meat products are the main products, and secondary products are blood, bone, offal, raw fat, horned raw materials, hides, intestines, etc. More than 150 thousand tons of secondary resources are generated in the meat industry of Kazakhstan annually, which are mainly utilized. And this is the loss of valuable food and feed products, as well as medicines and light industry goods, but also huge monetary losses, leading to an increase in the cost of meat. Figure 6 shows the structure of deep processing of cattle slaughter products.
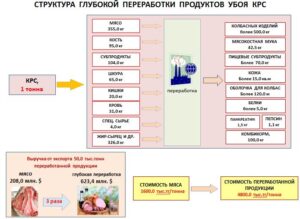
Figure 6 – Structure of deep processing of cattle slaughter products
For example, from 1 ton of slaughter mass of cattle worth 1.6 million tenge, with deep processing, you can get export-oriented products worth 4.8 million tenge. And this means that with the export of 50 thousand tons of processed products of the meat industry, the country could have 3 times more revenue.
Today, 40% of the population suffers from Lactase deficiency – this is a violation of the breakdown of lactose due to a deficiency of the enzyme lactase. The entire market of lactose-free dairy products in Kazakhstan is imported. Scientists of our institute have developed new technologies for lactose-free lactic acid food products based on mare’s, camel’s, goat’s and sheep’s milk. This made it possible to obtain new dietary products with high functional properties and rich in vitamins and minerals, and thereby expand the assortment of the National Brand (in the form of yoghurts, soft cheeses, whey drinks) (Fig. 7).

Figure 7 – Expansion of the assortment of the national brand of dairy products
The main goal of the development of the food and processing industry, we see in reducing the cost of production and increasing the export potential of agricultural raw materials and products of its processing.
Our institute offers for industrial testing resource-saving technologies for deep processing of raw materials of plant and animal origin. These technologies have undergone experimental approbation.
To increase the export potential of grain products, technologies have been developed for glucose-fructose syrups, protein feed additive for agricultural animals, obtaining amino acids, gluten-free bakery and confectionery products, pectin and inulin containing fruit and vegetable drinks.
To increase the export potential of the meat, dairy and fat-and-oil industries, such technologies have been developed for processing the gallbladder, new dairy products from camel, mare and sheep milk, hydrogenated and interesterified fats based on vegetable oils, whey drinks, etc.
Today, the Republic of Kazakhstan is taking measures to strengthen its position in ensuring food security. An important aspect in solving the problem of food security is: the introduction of effective technologies in order to increase the competitiveness of domestic products, ensure the required volume of domestic production, and form a state food reserve; taking measures to improve the system of economic relations in the field of production, public procurement, further processing, storage, transportation, sale of agricultural products, expansion of the material and technical base of agriculture.
Consequently, one of the main tasks of the supporting blocks of the innovation system of the agro-industrial complex is to create favorable conditions for the formation of a fund of innovations and their development in production while smoothing out the existing differences between the results obtained in production and the potential of scientific and technical developments. This refers to both the available and available to consumers a quantitative set of innovations, and their ability to improve production, economic and other indicators of agro-industrial activity.

